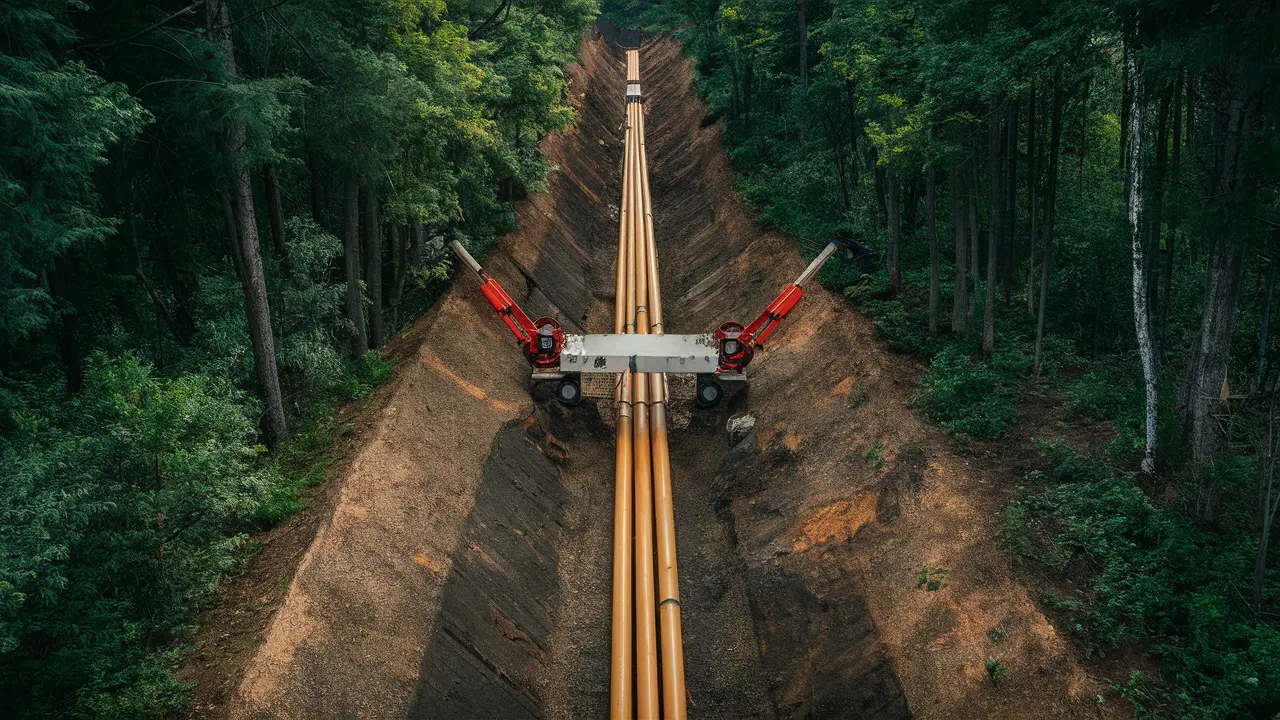
When the substratum of our bustling cities – the complex network of pipes and conduits that make modern life possible – requires attention, it is a moment for both challenge and innovation. The traditional method of excavating vast tracts of land to access these underground lifelines is not just inconvenient; it’s a throwback to an earlier age that knew no better. Enter trenchless pipe repair, a suite of technologies embraced by entities such as San Diego pipelining, which promises a less invasive, more efficient way to mend the arteries and veins of our urban landscapes. Such a method involves intricate work beneath the surface, requiring specialist knowledge and precision engineering. This content provides an informative guide to understanding the various trenchless pipe repair techniques and their benefits to urban infrastructure maintenance.
What is Trenchless Pipe Repair?
Trenchless pipe repair is an umbrella term for various methods that allow for the repair or replacement of underground pipelines without the necessity for large-scale, disruptive excavation work. This process is not just limited to small-scale residential work; it is eminently suitable for municipal and industrial applications, offering a way to address faults in water, sewage, and gas pipelines quickly and effectively. The root of this technology lies in minimizing the physical impact on the installation site, be it a bustling city street or a homeowner’s prized garden, all while ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of the utility being serviced.
The Various Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair
The spectrum of trenchless repair techniques available is broad, reflecting the varied nature of the pipelines they seek to mend. Cured-in-place pipe (CIPP) lining, perhaps the most widely known of these techniques, involves inserting a resin-coated liner into the existing pipe. Under pressure and heat, the resin cures, forming a new pipe within the old one that can last several decades. Pipe bursting replaces old pipes by breaking them and immediately laying new ones in their place without excavating along the pipe’s entire stretch. Slip lining, while one of the oldest methods, is still employed in suitable scenarios. A new, typically smaller diameter pipe is drawn into the damaged line and grouted in place, essentially slipstreamed within the failing conduit.
Advantages of Trenchless Pipe Repair
The advantages of choosing trenchless pipe repair over traditional methods are manifold. The obvious benefit, of course, is the drastically reduced disruption to the surrounding landscape. Without extensive digging, repair teams can operate with greater flexibility, often completing tasks within a day or two – a far cry from the weeks or months that extensive excavations might entail. This pace minimizes the inconveniences to nearby residents and businesses. Moreover, without the need for significant restorative landscaping post-repair, there are additional cost savings. In the long term, reducing repair-related disturbance also translates into societal savings, as traffic flows are less affected and commerce can continue unabated.
Considerations When Choosing a Trenchless Repair Method
Selecting the correct technique for trenchless repair is crucial for the project’s success. Factors to consider include:
- The age and material of the existing pipes
- The extent and type of damage incurred
- The geological makeup encompassing the infrastructure
Expert evaluation is indispensable. It ensures that the proposed method aligns with the specific repair requirements and reduces the risk of subsequent complications.
Trenchless Technology and Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of trenchless technology are substantial and well-documented. The reduction in topsoil disruption prevents the local ecosystem disturbance typically associated with traditional excavation methods. Furthermore, trenchless repairs generally require fewer raw materials, generating less waste. The Environmental Protection Agency’s findings emphasize the positive environmental impact of CIPP, indicating a clear preference for these methods over more intrusive options.
The Role of Technology and Innovation in Trenchless Repairs
Technological advancements continue to refine the precision and efficiency of trenchless pipe repair. High-definition cameras enable real-time inspection within pipes, ensuring repairs are targeted and effective. Innovative materials for liners, such as fiberglass and UV-curable resins, extend the life of the repairs, providing a non-corrosive and wear-resistant infrastructure solution that offers a significant return on investment.
Potential Limitations and Considerations of Trenchless Repairs
While trenchless repairs have many merits, it is essential to acknowledge that they may not be universally applicable. Circumstances such as severe pipe collapse, certain pipe materials, or extreme environmental conditions can present challenges that trenchless methods cannot address. In these cases, traditional excavation may still be required. Thus, a professional and in-depth assessment is crucial to selecting a repair method, ensuring that trenchless technology is employed appropriately and effectively.
The Future of Pipe Repair: Trends and Predictions
As municipalities and service providers look toward the future, the trends in pipe repair are leaning increasingly toward less disruptive and more cost-effective technologies. The evolution towards more intelligent, data-driven repair solutions is poised to provide significant benefits. A promising example of the industry’s direction is found in a scholarly analysis of trenchless technology, which provides a comprehensive insight into its applicability in urban settings, highlighting the progressive nature of the field.
In conclusion, trenchless pipe repair symbolizes progress in urban utility management, blending enhanced efficiency with a responsible approach to environmental stewardship. While the initial costs may present a hurdle for some decision-makers, the long-term financial and ecological benefits make trenchless solutions advantageous. As technology evolves and municipalities adopt increasingly progressive maintenance strategies, trenchless repairs will likely become the benchmark for subsurface utility work.